7 June 2011
WASHINGTON—New research focusing on the Houston area suggests that widespread urban development alters weather patterns in a way that can make it easier for pollutants to accumulate during warm summer weather instead of being blown out to sea.
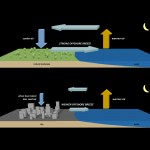
Paved surfaces in the Houston area keep the city warmer than more natural surfaces. As a result, overnight temperatures are often similar between the city and nearby offshore areas, which weakens summertime breezes and enables air pollution to build up. The stagnant conditions also persist during the day because of larger-scale wind patterns.
© University Corporation for Atmospheric Research
The international study could have implications for the air quality of fast-growing coastal cities in the United States and other midlatitude regions overseas. The reason: the proliferation of strip malls, subdivisions, and other paved areas may interfere with breezes needed to clear away smog and other pollution.
The research team combined extensive atmospheric measurements with computer simulations to examine the impact of pavement on breezes in Houston. They found that, because pavement soaks up heat and keeps land areas relatively warm overnight, the contrast between land and sea temperatures is reduced during the summer. This in turn causes a reduction in nighttime winds that would otherwise blow pollutants out to sea.
In addition, built structures interfere with local winds and contribute to relatively stagnant afternoon weather conditions.
“The developed area of Houston has a major impact on local air pollution,” says scientist Fei Chen of the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colo. and lead author of the new study. “If the city continues to expand, it’s going to make the winds even weaker in the summertime, and that will make air pollution much worse.”
While cautioning that more work is needed to better understand the impact of urban development on wind patterns, Chen says the research can eventually help forecasters improve projections of major pollution events. Policy makers might also consider new approaches to development as cities work to clean up unhealthy air.
The article will be published this month in the Journal of Geophysical Research- Atmospheres, a publication of the American Geophysical Union.
Houston, known for its mix of petrochemical facilities, sprawling suburbs, and traffic jams that stretch for miles, has some of the highest levels of ground-level ozone and other air pollutants in the United States. State and federal officials have long worked to regulate emissions from factories and motor vehicles in an effort to improve air quality.
The new study suggests that focusing on the city’s development patterns and adding to its already extensive park system could provide air quality benefits as well.
“If you made the city greener and created lakes and ponds, then you probably would have less air pollution even if emissions stayed the same,” Chen explains. “The nighttime temperatures over the city would be lower and winds would become stronger, blowing the pollution out to the Gulf.”
Chen adds that more research is needed to determine whether paved areas are having a similar effect in other cities in the midlatitudes where sea breezes are strongest. Coastal cities from Los Angeles to Shanghai are striving to reduce air pollution levels. However, because each city’s topography and climatology is different, it remains uncertain whether expanses of pavement are significantly affecting wind patterns.
For the Houston study, Chen and his colleagues focused on the onset of a nine-day period of unusually hot weather, stagnant winds, and high pollution in the Houston-Galveston area that began on August 30, 2000. They chose that date partly because they could draw on extensive atmospheric measurements taken during that summer by researchers participating in a field project known as the Texas Air Quality Study 2000. That campaign was conducted by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, the U.S. Department of Energy, universities, and the Texas Natural Resource Conservation Commission.
In addition to the real-world measurements, the study team created a series of computer simulations with NCAR’s Advanced Weather Research and Forecasting model.
Fei and his colleagues focused on wind patterns, which are driven by temperature contrasts between land and sea. If, as in one of the computer simulations, Houston were covered with cropland instead of pavement, inland air would heat up more than marine air during summer days, causing a sea breeze to blow onshore in the afternoon. Conversely, as the inland air became cooler than marine air overnight, a land breeze would blow offshore—potentially blowing away pollution.
In contrast, the actual paved surfaces of Houston absorb more heat during the day and are warmer overnight. This results in stagnation for three reasons:
- At night, the city’s temperatures are similar to those offshore. The lack of a sharp temperature gradient has the effect of reducing winds.
- During the day, the hot paved urban areas tend to draw in air from offshore. However, this air is offset by prevailing wind patterns that blow toward the water, resulting in relatively little net movement in the atmosphere over the city.
- Buildings and other structures break up local winds far more than does the relatively smooth surface of croplands or a natural surface like grasslands. This tends to further reduce breezes.
“The very existence of the Houston area favors stagnation,” the article states.
The study also found that drought conditions can worsen air pollution. This is because dry soil tends to heat up more quickly than wet soil during the day. It releases more of that heat overnight, reducing the temperature contrast between land and water and thereby reducing nighttime breezes.
By comparing observations taken in 2000 with computer simulations of Houston-area winds and temperatures, the researchers were able to confirm that the Advanced Weather Research and Forecasting model was accurately capturing local meteorological conditions.
The research was funded by the U.S. Air Force Weather Agency, the U.S. Defense Threat Reduction Agency, and the National Science Foundation.
AGU Contact:
Peter Weiss, Phone: +1 202 777 7507, E-mail: [email protected],
NCAR/UCAR Contact
David Hosansky, Phone: +1 303 497 8611, E-mail: [email protected]
As of the date of this press release, the paper by Chen et al. is still “in press” (i.e., not yet published). Journalists and public information officers (PIOs) of educational and scientific institutions who have registered with AGU candownload a PDF copy of this paper in press.
Or, you may order a copy of the paper by emailing your request to Peter Weiss at [email protected]. Please provide your name, the name of your publication, and your phone number.
Neither this paper nor this press release are under embargo.
“A numerical study of interactions between surface forcing and sea-breeze circulations and their effects on stagnation in the greater Houston area”
Fei Chen, Mukul Tewari
National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado, USA;
Shiguang Miao
Institute of Urban Meteorology, China Meteorological Administration, Beijing, China;
Jian-Wen Bao
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Boulder, Colorado, USA;
Hiroyuki Kusaka
Center for Computational Sciences, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Japan
Fei Chen, NCAR Scientist: [email protected], +1 (303) 497-845