Research finds N95 respirators may reduce hospitalizations from wildfire smoke by about 30%, but synthetic, cotton and surgical facemasks are less effective at protecting against fine particles in smoke.
28 September 2021
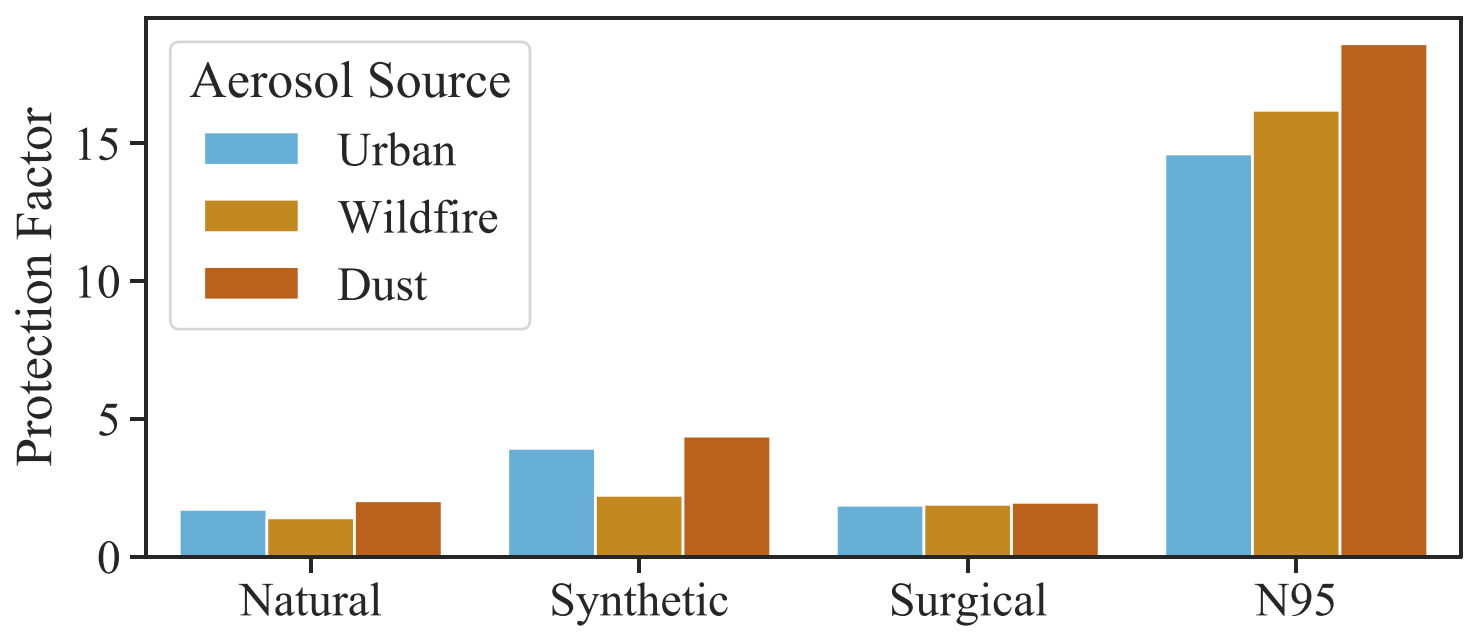
Researchers calculated a “protection factor” for each type of face covering based on its ability to filter out particles and the amount of air that likely leaks around the mask. Credit: Kodros et al./GeoHealth
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, +1 (202) 777-7492, [email protected] (UTC-4 hours)
Contact information for the researchers:
Jack Kodros, Colorado State University, [email protected] (UTC-6 hours)
WASHINGTON—N95 respirators offer the best protection against wildfire smoke and other types of air pollution, performing better than synthetic, cotton and surgical masks.
Researchers performed lab experiments to investigate the ability of different face masks and respirators to filter out particles in a range of sizes found in smoke and air pollution. They placed the different mask materials over a pipe that “breathes” in air and particles inside a plastic box.
N95s were so effective in the lab experiments that the researchers estimate their widespread use could reduce hospital visits attributable to wildfire smoke by 22% to 39%. The study’s findings can provide evidence-based recommendations to help people protect themselves during wildfire season.
The new study was published in GeoHealth, AGU’s journal investigating the intersection of human and planetary health for a sustainable future.
Climate change has made wildfires more frequent and intense in the Western U.S., and the resulting smoke exposure is taking a toll on people’s health. Wildfire smoke contains tiny particles smaller than 2.5 microns in diameter (PM2.5) — about the size of a single bacterium — that enter the lungs and are linked to multiple health problems, including a higher risk of asthma, respiratory infections and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Face coverings have become second nature to many people during the coronavirus pandemic, making some wonder if masks and respirators could also protect against smoke and pollution. By definition, respirators are tight-fitting protective equipment that seal around the nose and mouth to filter the air coming in and out. Surgical-style face masks are designed to capture the droplets and particles produced by the wearer to prevent the spread of disease.
“People were asking, should we keep them on in the summer when the fire season starts?” said Jack Kodros, an atmospheric scientist at Colorado State University and lead author on the new study. “There weren’t a lot of guidelines on what sort of masks would be helpful for wildfire smoke.”

Researchers compared how much protection different mask types provided from smoke and other aerosols. N95 masks provided the best protection.
Credit: AGU
Kodros and his team measured how well N95 respirators and synthetic, cotton and surgical masks each filter out the sizes of particles found in air pollution. Then they calculated how much each face covering would reduce exposure to pollution by considering their ability to filter the particles, and how much air the masks are likely to leak when attached to a person’s face.
They found that N95s offer the best protection against wildfire smoke, reducing a person’s exposure by a factor of 16. Synthetic and cotton masks do a poor job of filtering out the particle sizes found in wildfire smoke, and only reduced exposure by a factor of 2.2 and 1.4, respectively. Surgical masks filter more than 90% of the particles but previous research has shown they let about 50% of the air leak around the mask, making them only about as effective as the synthetic and cotton options.
N95s also worked best against larger dust particles and urban air pollution, which contains particles from car exhaust that are even smaller than particles from wildfire smoke.
Reducing Hospitalizations from Wildfire Smoke
In the second part of their study, the researchers estimated the benefits of mask wearing across an entire population. They developed a model that took into account the percentage of people likely to wear masks and how consistently they would wear them. They applied the model to the 2012 Washington state fire season to see if mask wearing would have changed the number of hospitalizations due to respiratory problems.
The model suggested that N95s would have prevented about 30% of the hospital visits from wildfire smoke. Surgical masks and synthetic masks would have reduced visits by about 17% and 13%, respectively, while cotton masks would have caused only a 6% reduction.
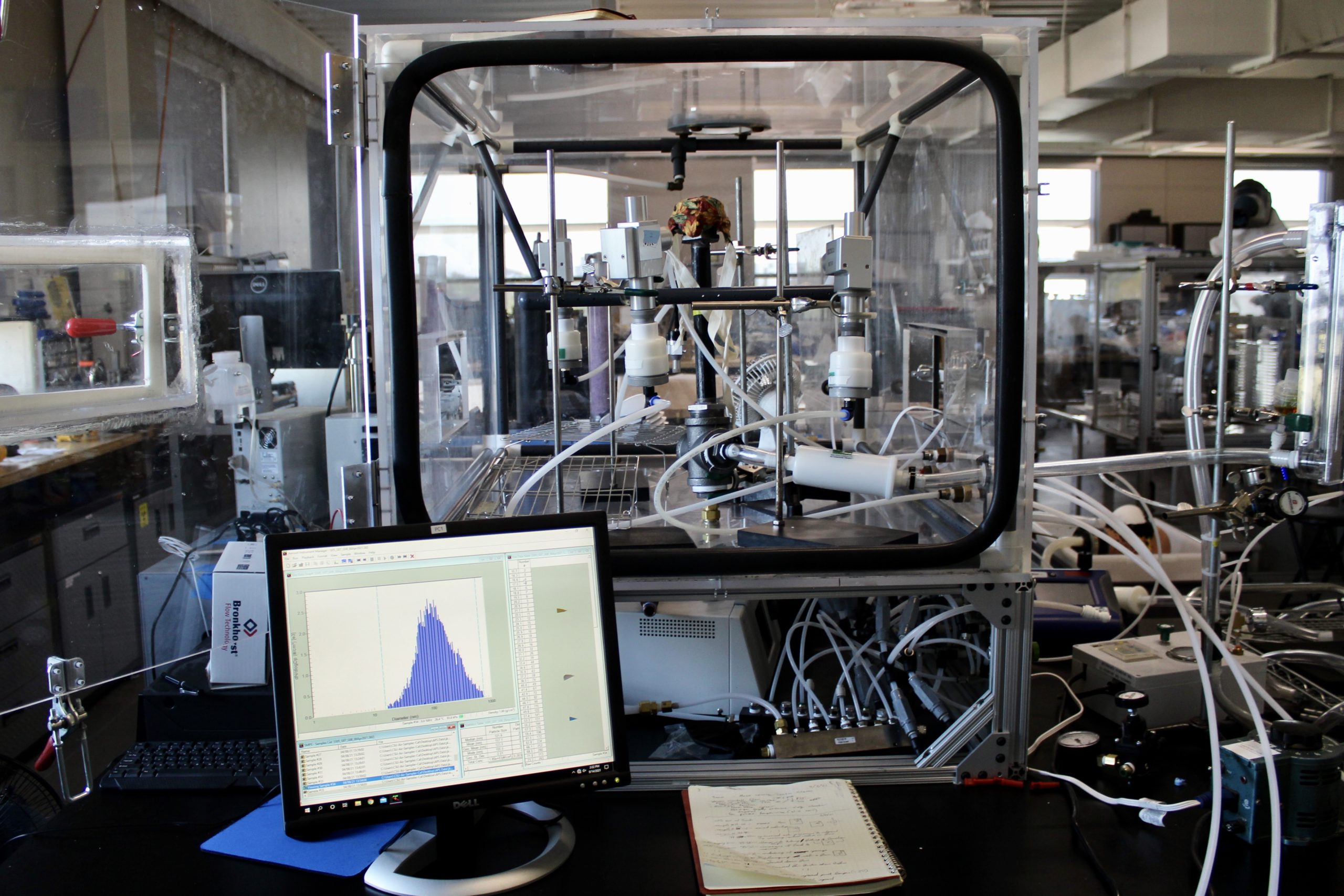

Caption: Researchers at Colorado State University use this chamber to test how well masks and respirators filter out particles from the air.
Credit: Jack Kodros
Kodros emphasizes that these mask recommendations are specific to air pollution and do not apply to the coronavirus. “For COVID-19, you’re wearing a mask to protect yourself and also to reduce your own emitted droplets,” he said. Fabric masks have been shown to be effective for public health during the current crisis and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends the use of masks with two or more layers of fabric that fit snugly over the nose and mouth.
Stephanie Holm, a pediatrician, environmental epidemiologist and co-director of the Western States Pediatric Environmental Health Specialty Unit at the University of California, San Francisco, says that currently there is a lot of interest—but also a lot of confusion—about how well different mask materials filter out particles. “I think this particular study fills a nice gap in terms of thinking about how we translate that kind of filtration data into real levels of protection, and real differences in health effects that we could see in a population,” she said.
Holm was not involved in the study, but she frequently advises families on how to protect themselves from wildfire smoke and is excited to incorporate this information into her recommendations.
###
AGU (www.agu.org) supports 130,000 enthusiasts to experts worldwide in Earth and space sciences. Through broad and inclusive partnerships, we advance discovery and solution science that accelerate knowledge and create solutions that are ethical, unbiased and respectful of communities and their values. Our programs include serving as a scholarly publisher, convening virtual and in-person events and providing career support. We live our values in everything we do, such as our net zero energy renovated building in Washington, D.C. and our Ethics and Equity Center, which fosters a diverse and inclusive geoscience community to ensure responsible conduct.
Notes for Journalists:
This research study is published with open access and is freely available. Download a PDF copy of the paper here. Neither the paper nor this press release is under embargo.
Paper title:
“Quantifying the Health Benefits of Face Masks and Respirators to Mitigate Exposure to Severe Air Pollution”
Authors:
John K. Kodros, (corresponding author), Christine L’Orange, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA
Katelyn O’Dell, Jeffrey R. Pierce, Department of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA
Jonathan M. Samet, Department of Environmental & Occupational Health, Colorado School of Public Health, Aurora, CO, USA
John Volckens, Department of Mechanical Engineering and Department of Environmental and Radiological Health Sciences, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA