The ancient drought around 1,800 years ago had just 68% of today’s streamflow volumes, tree rings reveal, marking an unprecedented dry period in the western US
9 June 2022
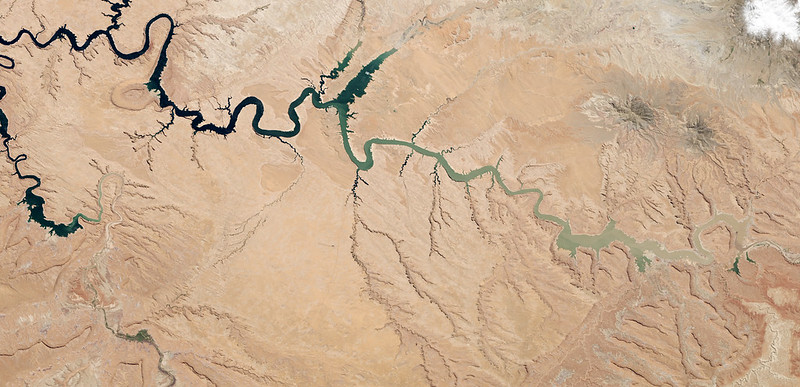
Lake Powell, a major reservoir along the Colorado River, was at less than half its capacity in 2014. A new study, published in Geophysical Research Letters, used tree rings to uncover the most severe drought in 2,000 years of the river’s history. Credit: NASA Goddard/Earth Observatory
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, [email protected], +1 (202) 777-7492 (UTC-4 hours)
Bureau of Reclamation press contact:
Peter Soeth, [email protected], +1 (303) 445-3615 (UTC-6 hours)
WASHINGTON—The ongoing severe drought in the Colorado River Basin has led to the river flowing at 84% of its historic average flow. An even more intense “megadrought” hit the region around 1,800 years ago, a new study reveals. At just 68% of the river’s average flow rate, the megadrought is the most severe drought discovered in the arid region yet.
The new study, published in the AGU journal Geophysical Research Letters, used tree-ring data and other climate records to identify a drought period unmatched in severity by the current drought or other ancient droughts. It reveals a greater range of natural hydroclimatic variability in the Colorado River than previously recognized, highlighting a need for water managers to adjust expectations and prepare for even more intense drought.
“Previous studies have been limited to the past 1,200 years, but there are a limited number of paleorecords of moisture variability available back 2,000 years,” said Subhrendu Gangopadhyay, lead study author and an engineer at the Bureau of Reclamation. “While there has been research that shows extended dry periods in the southwest back to the eighth century, this reconstruction of Colorado River streamflow extends nearly 800 years further into the past.”
The research found that compared to the current 22-year drought in the Colorado River, with only 84% of the instrumental period (1906–2021) average flow at the Lees Ferry gage, the flow during a 22-year period in the second century was much lower, just 68% of this average flow.
“Although tree-ring data are sparse back to the second century, this extreme drought event is also documented in paleoclimatic data from lakes, bogs and caves,” said Connie Woodhouse, a professor at the University of Arizona and a study co-author.
“It’s quite compelling from the available tree-ring data that the second century experienced an extraordinarily severe drought, highly persistent, and very intense. It’s quite remarkable,” said Edward Cook, a dendochronologist at Columbia University.
The future of western water
Water managers may use this new extended dataset to understand past droughts better and plan for future droughts.
“The results of this work can provide water managers with an increased understanding of the range of flow variability in the Colorado River,” added Gangopadhyay. “It should provide information to help water managers during this drought and plan for even more persistent and severe droughts than previously considered.”
“For future work, collection and analysis of more remnant wood can provide further documentation of this second century drought,” added Woodhouse.
The ongoing Colorado River Basin drought has extensive impacts throughout the West, including water shortages for homes and crops and decreased generation of hydroelectric power. The new knowledge for how much worse droughts can be, even without anthropogenic climate forcing, points to a potentially grim outlook for water in the West.
“Megadroughts happened naturally in the past, before elevated greenhouse gases. It’s kind of scary that the West may have slipped into a new megadrought that might have happened anyway, but is now made worse because of greenhouse gas forcing,” said Cook.
# # #
AGU (www.agu.org) supports 130,000 enthusiasts to experts worldwide in Earth and space sciences. Through broad and inclusive partnerships, we advance discovery and solution science that accelerate knowledge and create solutions that are ethical, unbiased and respectful of communities and their values. Our programs include serving as a scholarly publisher, convening virtual and in-person events and providing career support. We live our values in everything we do, such as our net zero energy renovated building in Washington, D.C. and our Ethics and Equity Center, which fosters a diverse and inclusive geoscience community to ensure responsible conduct.
Notes for Journalists:
This research study will be available for free until 6/30. Download a PDF copy of the paper here. Neither the paper nor this press release is under embargo.
Paper information:
“Tree rings reveal unmatched 2nd century drought in the Colorado River Basin”
Additional note:
This research will be presented virtually at AGU’s Frontiers in Hydrology Meeting during two presentations on Wednesday, 22 June from 2:30 to 3:00 p.m. AST.
- Abstract 317-01: The Second-century Drought in the Colorado River Basin
- Abstract 317-02: A 2000-year Streamflow Time Series for the Colorado River at Lees Ferry, AZ
Press registration for #FIHM22 is free for both online and in-person attendees. The meeting runs from 19 to 24 June, 2022, online and in San Juan, Puerto Rico.
Authors:
- Subhrendu Gangopadhyay (corresponding author), Bureau of Reclamation, Denver, CO
- Connie A. Woodhouse (corresponding author), School of Geography, Development, and Environment, and Laboratory of Tree-Ring Research, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ
- Gregory J. McCabe (corresponding author), US Geological Survey, Water Mission Area – Integrated Modeling and Prediction Division, Denver CO
- Cody C. Routson, School of Earth and Sustainability, Northern Arizona University, Flagstaff, AZ
- David M. Meko, Laboratory of Tree-Ring Research, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ
Released jointly with the Bureau of Reclamation