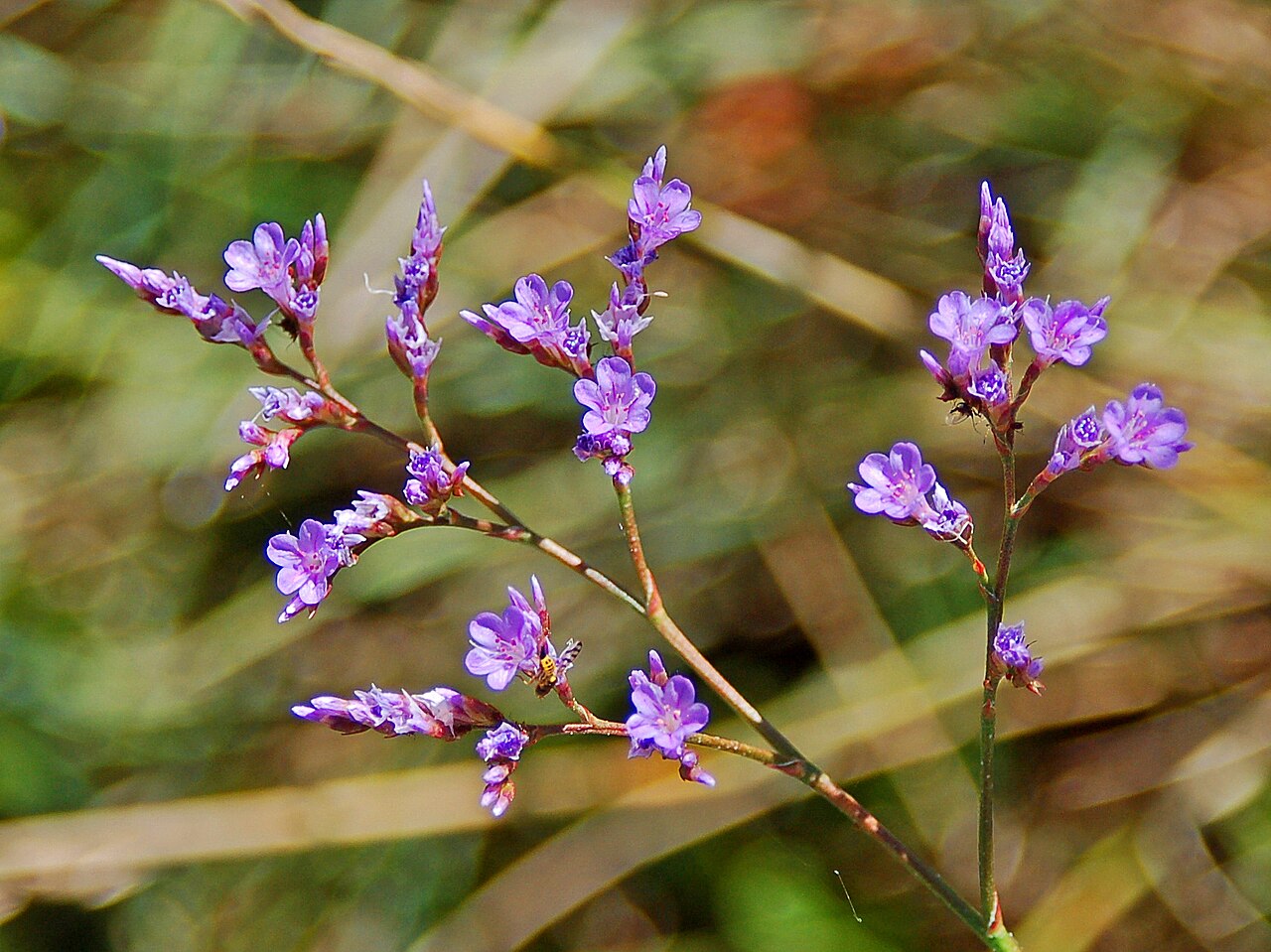
Flowers of Limonium narbonense, a species of sea lavender native to Mediterranean coasts. The plant’s hardy, extensive belowground structures make it adept at securely storing carbon, boosting the climate-mitigation services of the salt marshes where it often grows. Credit: Hectonichus, Wikimedia
AGU News
Press registration is open for the 2026 Ocean Sciences Meeting in Glasgow, Scotland
Staff, freelance and student journalists, press officers and institutional writers are eligible to apply for complimentary press registration for the conference, which will convene 22-27 February. [media advisory][OSM26 Press][eligibility guidelines][preview conference hotels]
Featured Research
This purple flower is a carbon-storing power player
Sea lavender, a genus of flowering plants common to coastal areas around the Mediterranean, may boost the carbon storage abilities of salt marshes. Researchers studying the distribution of biomass and carbon content in a salt marsh of Italy’s Venice Lagoon found a sea lavender species growing wherever carbon storage was highest, more so than six other common species they examined. The plant grows plenty of tough, woody mass underground that durably locks away carbon, the researchers explain, making it a valuable member of salt marsh communities. Because salt marshes trap and store carbon far more effectively than solid-land ecosystems, managing them sustainably matters for mitigating human-driven climate change. [JGR Biogeosciences study]
Arctic melting may hasten the loss of Antarctic ice, too
A domino-style series of connections and feedbacks between the poles means that Arctic ice loss may speed up Antarctic ice loss as well. Researchers used model simulations of climate and ice sheets to show that as northern ice caps diminish, the newly de-iced areas and the northern Atlantic Ocean warm up. That warmer water eventually circulates to the Southern Ocean, where it periodically washes up against the Antarctic coast and amplifies the retreat of the West Antarctic ice sheet, which scientists already consider especially vulnerable to ice loss from global warming. [Geophysical Research Letters study]
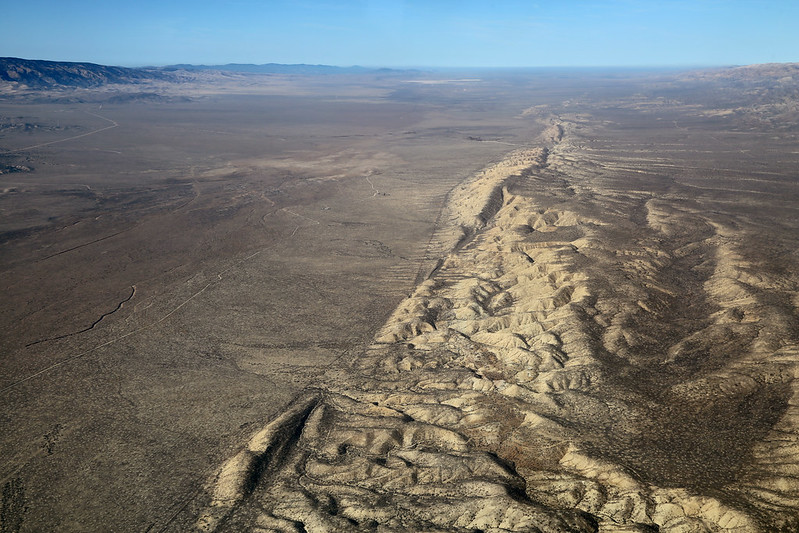
Drying of giant lakes helped awaken dormant tectonic faults
Over tens of thousands of years, declining water levels at three massive lakes helped activate nearby dormant faults on the Tibetan Plateau, according to a recent study. As the water weight lightens, the researchers say, Earth’s crust slowly rebounds upward, pushing on nearby faults and making them more prone to slippage. To quantify this process, the team studied lake shorelines for indicators of historical water levels, then used a plate tectonics model to estimate how the lightened water load would affect tectonic activity. About a fifth of fault movement near Nam Co Lake over the past 116,000 years stems from this phenomenon, they found, as does roughly 70 meters of vertical movement on the fault near the Yamzho Yumco and Puma Yumco lakes. [Geophysical Research Letters study]
Hydrogen-powered planes would leave more climate-friendly contrails
If future airplanes fly on hydrogen power, their contrails — not just their emissions — would be more climate-friendly than those of conventional kerosene-fueled planes, a recent study projects. When today’s planes fly through cold, humid air, the long, wispy contrails they leave behind can morph into clouds which act like heat-trapping “blankets” in the atmosphere, worsening the climate impact of flying. Researchers simulated how hydrogen-powered planes’ contrails would evolve over time in a range of atmospheric conditions. Contrails with fewer but larger ice crystals (as expected from hydrogen planes) faded more rapidly, partly because larger crystals drop out of the sky more quickly, reducing the overall climate impact. [JGR Atmospheres study]
Changing flight paths during space weather protects passengers from radiation
In May of 2024, a United Airlines flight from San Francisco to Paris protected those aboard from the radiation of a geomagnetic storm by altering its flight path. By comparing radiation levels recorded by onboard instruments against those estimated for a hypothetical flight that stayed on-route, researchers found that while the plane still received sporadic pulses of high radiation, the dosage would have been up to three times higher had it stayed the course. The story underscores the importance of considering alternate routes to protect passengers during space weather events like solar flares and coronal mass ejections, the team says, since Earth’s atmosphere and magnetic field provide less protection from these events’ radiation at high altitudes. [JGR Space Physics study]
Cooling crust births new subduction zones
Scientists still aren’t certain how subduction zones — boundaries where one tectonic plate slides under another — get started, partly because it’s unclear how the normally-rigid plates weaken enough to deform into such a system. In search of answers, researchers analyzed rocks from a nearly 500-million-year-old oceanic subduction zone in present-day Québec using high-resolution imaging. They found that cooling at the plate boundary altered the rocks’ mineral compositions and made grains smaller, enabling deformation — a counterintuitive result, since cooling typically strengthens rocks. While they haven’t yet pinpointed the cause of cooling, the team says this shows subduction can begin without a sudden release of built-up stress in oceanic crust. [JGR Solid Earth study]
Our oceans’ “natural antacids” act faster than we thought
New evidence from New Zealand suggests that calcium carbonate dissolution occurs not just over millennial timescales, but over annual and decadal ones too. [Eos research spotlight][AGU Advances study]
Which countries are paying the highest price for particulate air pollution?
Cutting air-polluting emissions 10% could save hundreds of thousands of lives and over a trillion dollars in the northern hemisphere each year, with the biggest benefits in China. [Eos research spotlight][GeoHealth study]